Bursitis

Appointment Inquiries
Call us at: (877) 222-5348
Definition
Inflammation of the fluid-filled pads (bursae) that act as cushions at the joints.
Root Causes
Achiness, Brusing, Rash, Redness, Reduced Range of Motion, Sharp Pain, Shooting Pain, Stiffness, Swelling, Tenderness
Risk Factors
Age, Diabetes, Gout, Hobbies, Infection, Injury, Obesity, Repetitive Motion Injury, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Workplace factors
Treatments
Medical Intervention, Physical Therapy, RICE
What is bursitis?
Bursitis is inflammation of a bursa. Bursae (plural for bursa) are small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones against the soft tissue of the body. They allow muscles, tendons, and skin near your joints to glide smoothly with bone. Their purpose is to reduce friction at stress points throughout the body.
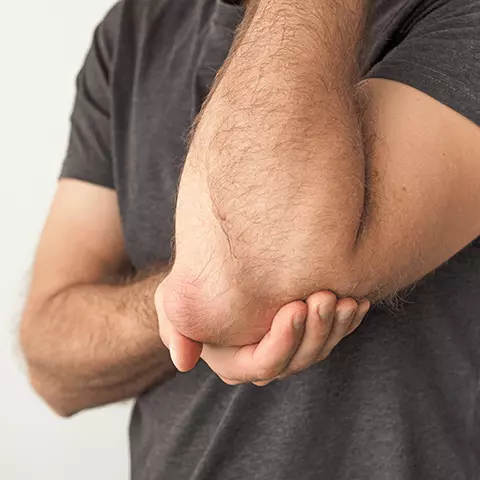
When a bursa becomes inflamed, it can create painful swelling around the affected joint and limit movement. This type of inflammation most commonly appears in the shoulders, elbows, knees, hips, and feet.
Types of bursitis
Bursitis can occur in any bursa in the body. In some cases, small nodules can be felt within the bursa.
Here are some of the most common types:
- Olecranon bursitis is bursa inflammation in the elbow, specifically on the outside or tip of the elbow a the olecranon process. It is often caused by injury.
- Prepatellar bursitis, or knee bursitis, is bursa inflammation in the front of the knee at the knee cap (patella). It often puts uncomfortable pressure on other moving parts of the knee. It is often caused by constant pressure from kneeling. It is common in plumbers, roofers, and gardeners.
- Retrocalcaneal bursitis, also known as ankle or achilles tendon bursitis, is inflammation of the sac between the heel bone and the achilles tendon. It can be very painful and swell greatly. It is most common in athletes.
- Trochanteric bursitis, or hip bursitis, is bursa inflammation at the greater trochanter. The trochanteric bursa is at the top of the femur outside of where your leg attaches to your pelvis. It can develop slowly and can appear alongside other medical conditions such as arthritis. It is often a result of injury and is more common in athletes.
Bursitis is usually an acute or temporary condition, but it can be chronic. Associated pain can also be constant or sporadic.
Symptoms of bursitis
Depending on the type of bursitis you have, different symptoms can occur. The general symptoms for all types are:
- Achiness
- Bruising
- Limited motion
- Rash
- Redness
- Sharp pain
- Shooting pain
- Stiffness
- Swelling
- Tenderness
All types of bursitis may also be accompanied by a fever, chills, or other symptoms of infection. Septic bursitis is usually caused by direct infection, such as from a cut, and it accounts for about 1/3 of cases. Septic bursae often become red, hot, or swollen.
Sudden difficulty or inability to move a joint is also a sign. For bursitis in the hips, knees, and feet, walking may also become difficult or painful. Touching the area may also make it hurt more.
Causes and risk factors of bursitis
The most common cause of bursitis is repetitive motions or positions that put pressure on the bursa around a joint. Injury and infection are also very common causes.
Occupations and hobbies that increase your risk of developing bursitis include:
- Carpentry
- Cleaners
- Gardening
- Painting
- Playing a musical instrument
- Roofers
- Shoveling
- Sports with clubs or rackets
- Sports with running
- Tile and carpet setting
Poor posture and improper exercise technique is also a major risk factor.
Anyone can develop this condition but age, hobbies, occupation, and being overweight increase your risk significantly. You are also at higher risk if you have rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or diabetes.
Bursitis treatment at BackFit
Most cases of bursitis get better on their own. The best initial treatment is to rest, ice, elevate, splint, and avoid the motion that caused the inflammation.
Rest will stop it from getting worse, prevent you from making it worse, and start the healing process. The resting period should last no longer than 48 hours. You can usually then start participating in modified activities.
Ice reduces pain from the increased blood flow from the inflammation. Apply ice 20 minutes on and 20 minutes off for up to 48 hours. Do not exceed 48 hours of ice because it may delay the healing process. Be sure to use a towel between your skin and the ice to prevent frostbite.
Elevation means to raise the affected area closer to or above heart level. For bursitis in the arm, you can simply hold your opposite shoulder. For bursitis in the leg, consider resting your foot on a stool. By elevating the affected area, it improves the venous return to your heart. Increased return can reduce both pain and swelling as well as increase healing rates.
Splinting is the use of a rigid or flexible device to maintain the position of the affected area. Splints can be as simple as a sling or tape or as complex as a custom brace. Splinting keeps the affected area from moving while it heals and helps prevent further injury.
You should seek medical attention if you have:
- Pain that interferes with your day-to-day activities.
- Redness, swelling, or warmth in the injured area.
- Soreness that doesn’t improve.
- Symptoms of bursitis accompanied by a fever.
You should also seek medical attention if you have repetitive bursitis or you have had pain, redness, swelling, or soreness at a joint for a long time.
Our medical care professionals at BackFit Health + Spine can help diagnose bursitis with a physical exam, x-rays, and ultrasounds. X-rays can exclude other causes for your pain. Ultrasounds are used to help identify bursitis when it cannot be easily identified with a physical exam.
Your custom treatment plan will be mainly focused on physical therapy. Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles in the affected area in order to help reduce pain and prevent reoccurrence. If we find that your bursitis has become infected or is caused by an infection, we will prescribe antibiotics to eliminate the infection.
In some cases, the doctor may inject corticosteroid injections. This will help to quickly decrease inflammation and pain so you can heal and recover so you can return to daily activities and life.
More About BackFit
Looking to learn more? Explore our locations, treatments, or our new patient offer below or contact one of the BackFit Family of staff to have your questions answered.